How to Ensure a Reliable Connection Effortlessly
In today’s fast-paced digital world, having a stable network is more important than ever. Whether you’re working on a critical project, transferring files, or simply browsing the web, a seamless link between your device and the server can make all the difference. Imagine trying to send an important file, only to face delays or interruptions. Frustrating, right?
This article will guide you through the essentials of maintaining a strong network. You’ll learn about key concepts like TCP, the three-way handshake, and how these components work together to ensure smooth data transfer. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of what makes a network stable and how to achieve it effortlessly.
Key Takeaways
- Understand why a stable network is crucial in today’s digital age.
- Learn the basics of TCP and its role in data transfer.
- Discover the importance of the three-way handshake in establishing connections.
- Explore how windowing and sequencing enhance network reliability.
- Gain insights into the differences between reliable and unreliable connection methods.
Understanding Reliable Connection: Basics and Benefits
A stable link between your device and the server is essential for seamless digital experiences. Whether you’re working on a project, streaming content, or transferring files, a dependable network ensures your tasks are completed without interruptions. But what exactly makes a connection reliable, and why does it matter?
What is a Reliable Connection?
A reliable connection ensures that data sent from one point reaches its destination without errors or loss. Protocols like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) play a crucial role in this process. They use techniques such as the three-way handshake to establish a secure link between devices. This guarantees that your information arrives intact, even if it takes a bit longer.
The Role of Stable Networks in Everyday Use
Stable networks are the backbone of modern digital activities. From streaming high-definition videos to sending large files, they ensure smooth performance. Here’s how they impact your daily tasks:
- Streaming: Buffering-free videos and uninterrupted music.
- File Transfers: Quick and secure delivery of important documents.
- Online Communication: Clear video calls and instant messaging.
Additionally, reliable networks minimize data loss and enhance security. They ensure that sensitive information, like financial data, is transmitted safely. This is especially important in professional settings where accuracy and confidentiality are critical.
| Aspect | Reliable Connection | Unreliable Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Data Delivery | Guaranteed | Not Guaranteed |
| Speed | May be slower due to checks | Faster but prone to errors |
| Security | High | Low |
Understanding the difference between reliable and unreliable connections helps you make informed decisions about your network setup. While reliable connections may take more time, they ensure your data is safe and complete.
Technical Insights into TCP and the Three-Way Handshake
Behind every successful file transfer or streaming session is a well-established network protocol. TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, is the backbone of this process. It ensures that data moves smoothly between devices, even over long distances.
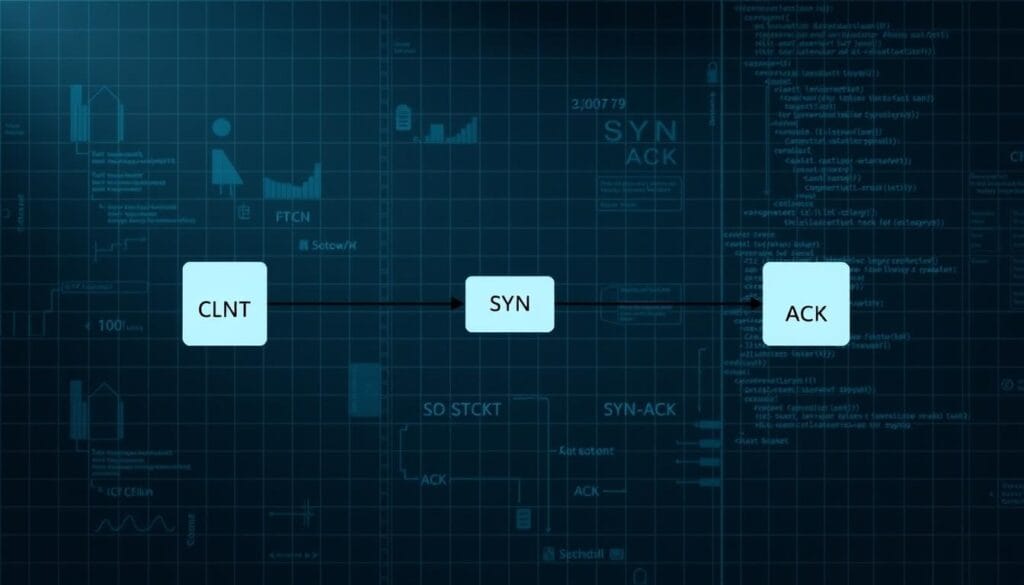
How TCP Establishes a Connection
TCP works by creating a secure link between two devices, such as your computer and a server. Before any data is sent, both devices must agree on the rules of the exchange. This is where the three-way handshake comes into play.
The handshake begins with a SYN (synchronize) message from the sender. The receiver responds with a SYN/ACK (synchronize/acknowledge) message. Finally, the sender sends an ACK (acknowledge) to confirm the connection. This process ensures both devices are ready to exchange data.
The Process of the Three-Way Handshake
Let’s break down the three steps of the handshake:
- SYN: The sender initiates the connection by sending a SYN message to the receiver.
- SYN/ACK: The receiver acknowledges the request and sends a SYN/ACK message back.
- ACK: The sender confirms the connection with an ACK message, and data transfer begins.
This method guarantees that both devices are active and ready to work together. It also allows them to negotiate parameters like window size and sequence numbers, which optimize data transfer.
For example, when transferring a file from PC-1 to PC-2, the handshake ensures that both devices are synchronized. This minimizes errors and ensures the file arrives intact, even if it takes a bit more time.
Diving into Connection Components: Windowing and Sequencing
Efficient data transfer relies on intricate mechanisms like windowing and sequencing. These components ensure that information moves smoothly across networks, even under challenging conditions. By understanding how they work, you can appreciate the balance between speed and stability in data transmission.
How Windowing Controls Data Flow
Windowing is a technique used to manage the amount of data sent before receiving an acknowledgment. It prevents network congestion by limiting the number of segments transmitted at once. For example, if the window size is set to 5, only five data segments are sent before waiting for a confirmation.
This approach ensures that the network doesn’t get overwhelmed. It also allows the receiver to process data efficiently, reducing the risk of errors or delays. Adjusting the window size can optimize performance based on network conditions.
Tracking Data with Sequence Numbers
Sequence numbers play a crucial role in maintaining data integrity. Each segment of data is assigned a unique number, allowing the receiver to identify and arrange them in the correct order. This ensures that even if segments arrive out of sequence, they can be reassembled accurately.
For instance, if segments 1, 2, and 3 are sent, but segment 2 arrives last, the sequence numbers help the receiver reconstruct the original data. This process minimizes errors and ensures complete data delivery.
Managing Data Loss and Retransmission
Data loss is inevitable in any network, but TCP handles it effectively. When a segment is lost, the receiver detects the gap in sequence numbers and requests retransmission. The sender then resends the missing segment, ensuring no data is permanently lost.
This method guarantees that your information arrives intact, even in less-than-ideal network conditions. It’s a critical feature for applications like file transfers or video streaming, where data accuracy is essential.
| Feature | Windowing | Sequencing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Controls data flow | Tracks data segments |
| Benefit | Prevents congestion | Ensures data integrity |
| Example | Limits segments sent | Reorders out-of-sequence data |
By mastering these components, you can enhance your network’s performance and reliability. Small adjustments in TCP settings can make a significant difference in how your data travels across the web.
Comparing Reliable vs. Unreliable Connections
Choosing the right method for data delivery can significantly impact your network’s performance. Reliable methods, like TCP, ensure data arrives intact but may take more time. Unreliable methods, such as UDP, prioritize speed but may sacrifice accuracy. Understanding when to use each approach is key to optimizing your network.

Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Reliable connections, like those using TCP, guarantee data delivery. They use mechanisms like the three-way handshake to establish a secure link. However, this process adds overhead, making it slower. Unreliable connections, like UDP, skip these steps, offering faster data transfer but with no guarantee of delivery.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- Reliable Connections: Ideal for file transfers, where accuracy is critical.
- Unreliable Connections: Best for real-time applications like video streaming or gaming.
Understanding Connectionless Data Delivery
Connectionless methods, such as UDP, are efficient for short data queries. For example, DNS resolution uses UDP to quickly retrieve domain information. Since these queries are small and frequent, the lack of guaranteed delivery is acceptable. This approach saves time and reduces network load.
Here’s when connectionless delivery makes sense:
- Short Queries: DNS lookups or quick status checks.
- Real-Time Applications: Video calls or online gaming, where speed is crucial.
By understanding these methods, you can choose the right approach for your needs. While reliable connections are robust, they may not always be the fastest option.
Ensuring Reliable Connection: Expert Tips and Best Practices
Maintaining a strong and secure network requires both proactive measures and smart optimizations. Whether you’re managing a small home setup or a large corporate system, these expert tips will help you safeguard your link and enhance performance.
Securing Your Connection Against Interruptions
Interruptions can disrupt your workflow and lead to data loss. To minimize these risks, consider the following strategies:
- Design Client Session State Caches: Store session data locally to handle intermittent connectivity. This ensures your work continues smoothly even if the network link breaks.
- Use Backup Connection Methods: Implement failover systems like secondary internet providers or mobile hotspots. This keeps your server accessible during outages.
- Monitor Network Health: Regularly check for issues like latency or packet loss. Early detection allows you to address problems before they escalate.
Optimizing Network Settings for Performance
Fine-tuning your network settings can significantly improve speed and stability. Here’s how to optimize your setup:
- Adjust TCP Parameters: Modify settings like window size and retransmission timers to match your network’s needs. This reduces delays and improves data flow.
- Prioritize Critical Traffic: Use Quality of Service (QoS) to ensure essential applications receive bandwidth first. This is especially useful for time-sensitive tasks like video calls.
- Upgrade Hardware: Invest in modern routers and switches that support advanced features. This enhances your network’s capacity and reliability.
By implementing these practices, you can maintain a high level of performance even under adverse conditions. A well-optimized network ensures your data moves efficiently, keeping your operations running smoothly.
Conclusion
Understanding the technical and practical aspects of network stability ensures your digital tasks run smoothly. From the three-way handshake to windowing and sequencing, TCP mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining a secure and efficient link between your device and the server.
Stability in network performance is crucial for data integrity and seamless operations. By applying expert tips like adjusting TCP parameters and prioritizing critical traffic, you can optimize your setup for better results.
Whether you’re transferring files or streaming content, knowing the trade-offs between reliable and unreliable methods helps you make informed decisions. Apply these principles to ensure your connection remains robust in any situation.



